In the fascinating world of Artificial Intelligence (AI) where machines evolve and surprise us with their abilities, have you ever wondered how your virtual assistant understands your commands? Or how do recommendation systems on streaming platforms recommend accurately content that matches your interest? Here we will deep dive into the minds of machines, and understand their thoughts and intentions, step by step, exploring the amazing possibilities with AI. Join this journey where we will explore the secrets and inspiring visions of a future where technology meets humanity.
We begin this journey by understanding two main types of AI: Capability AI and Functional AI and its subtypes, as shown below:
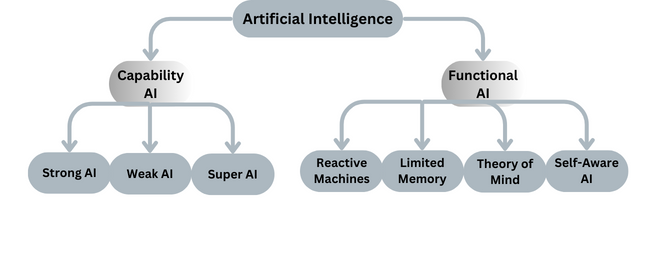
CAPABILITY AI:
Strong AI
Goal: To create machines like humans, who can learn like a human child, learn things by observing others, and build things on their own experience.
Imagine that you have a robot that not only speaks multiple languages fluently but also understands jokes, learns new languages, and even can paint beautiful artwork.
Such a type of AI that can understand, learn, and apply knowledge to solve problems like humans is known as Strong AI.
Example: Currently, we do not have real-life examples of Strong AI, it’s far away from now but we are making significant improvements in achieving this as researchers are working actively on it.

Weak AI (Narrow AI):
Goal: Designed to do a specific task.
Imagine you have a language translation app on your phone.
This app is incredibly good at translating text or speech from one language to another. However, it does not understand the meaning behind the words – it just matches patterns and translates based on predefined rules.
This type of AI is designed for a specific task and does not have human-like understanding.
Weak AI finds its strength in its specificity, it operates within predefined boundaries which makes it cost-effective and efficient for specific tasks. It might lack human understanding but its ability to excel in a particular domain makes it the most recognizable and widely used technology in today’s technology world.
Examples: Siri and Alexa are great examples of Weak AI. It can answer questions and perform tasks, yet it does not truly understand your queries – it simply follows predefined algorithms to respond accurately. Similarly, Self-driving cars navigate roads, and gaming bots play complex games are also an example of Weak AI.

Super AI:
Goal: To create Super Minds that are more capable than human minds in every aspect.
It is like Super Mind, which can surpass human intelligence in every aspect – creativity, problem-solving, emotional intelligence, and more.
This type of AI goes beyond the capability of the human mind in every aspect.
Currently, Super AI is a completely theoretical concept, but still, it raises ethical and existential questions about the future of humanity because of its boundless possibilities.
Example: You can find Such AI examples in science fiction movies like HAL 9000 from “2001: A Space Odyssey.” It is shown that HAL 9000 could think, plan, feel emotions like Humans and do things in a much better way than humans.

FUNCTIONALITY AI:
Reactive Machines:
Imagine a super smart robot, but he can only make decisions based on the information he has been programmed with. He cannot learn or improve with time.
They excel at specific tasks like playing chess or solving math problems but they cannot learn or think on their own.
They just do what they are programmed to do, and they do it very well.
Example: Calculator can be a reactive machine. It performs complex calculations, but it does not learn from the problems it solved and it cannot become better at math tomorrow because it solved problems today. You must input the numbers and the operations for it to work.
Recommendation Systems: Streaming platforms like Netflix or music apps like Spotify use reactive machines to suggest movies, shows, or songs you might like. They analyse your watching or listening history and recommend content based on what you have watched or heard before to improve your entertainment experience.
Online Search Engines: Have you ever wondered how search engines like Google get relevant results in a fraction of a second? Reactive Machines are working behind this. They follow predefined algorithms to match your search query with relevant web pages, ensuring that you get the information you need quickly and efficiently.
Weather forecasting tools, spam filters, and movie recommendations behind all this Reactive Machines are working to make our digital experience seamless.

Limited Memory:
Goal: To predict by analysing past information.
Memory AI can learn from past experiences and use that knowledge to make decisions.
It is like your smart friend who remembers your favourite pizza toppings.
These AI types, unlike reactive machines, have a memory bank. They do not just live in the present moment, they learn from their past, just like we do which forms the way for breakthroughs in natural language processing, image recognition, and reinforcement learning.
Limited Memory AI functions like our brain, and becomes smarter as it receives more data to train on. After the deep learning revolution in 2012, Limited AI was introduced and integrated into AI,s programming which enables it to make decisions based on both historical and real-time data.
Example: Limited Memory AI becomes a part of various practical applications. In self-driving cars, it predicts surrounding vehicle trajectories to ensure safe navigation.
Likewise in personalized online shopping, you will notice that the online store recommends products that seem like just made for you, these systems remember your browsing history, past purchases, and even items that you like. When you return to the website, they use this information to suggest products you may like, making your online shopping experience more interesting.
In chatbots, virtual assistants, and natural language processing systems, you will find the use of Limited AI in all those applications, where historical data work as a foundation to guide AI for prediction.

Theory of Mind:
Goal: To create machines that can understand human
It can understand human emotions, beliefs, and intentions. It is like giving a touch of humanity to machines enabling them to understand human feelings and intentions just like humans do.
For example, imagine that Alexa is not just a smart machine but she understands emotions, knows when you are happy or sad, and even guesses what you might be thinking if you are feeling down or upset then Alexa with her Theory of Mind capabilities, could play your favourite song or even share a funny story to cheer you up. This ability to understand human emotions, beliefs, and intentions makes Theory of Mind AI extraordinary and emotionally intelligent.
It’s like giving machines a heart and a soul.
We have not achieved it yet in the real world.
Example: Imagine robots helping children to learn social skills by recognizing their emotions. They understand human emotions and can respond accordingly. We are still in the early stage of development of this AI.

Self-Aware AI:
Goal: To create a machine with consciousness and own Identity.
Consider a computer program that not only understands human emotions but also has a sense of Self-Awareness. It’s like teaching a computer to look inside and find its feelings. It does not just process information but learns from its own experience. It’s like giving machines a sense of ‘self’, a form of consciousness.
Such AI would recognize its existence, thoughts, and emotions much like how human understands joy, sadness, or excitement. This self-awareness enables AI to respond or handle a situation with knowledge or depth of understanding like a friend or partner who knows how you feel without saying a word.
This is a more philosophical concept and it’s still far from now to become reality.
Example: Imagine a machine in the healthcare industry that understands its own maintenance needs, by understanding its functional limitations.